Dal-Bac Manufacturing, located strategically in Texas, is proud to serve clients nationwide. As part of our commitment to offering the best solutions in material bonding, we frequently get asked by West Coast customers about the differences between flame lamination and thermal fusing lamination. These two processes are pivotal in enhancing the durability and appearance of various materials, including paper, fabric, and foam. Let’s dive into the principles, benefits, and limitations of each method to help you determine which one might be best for your specific needs.
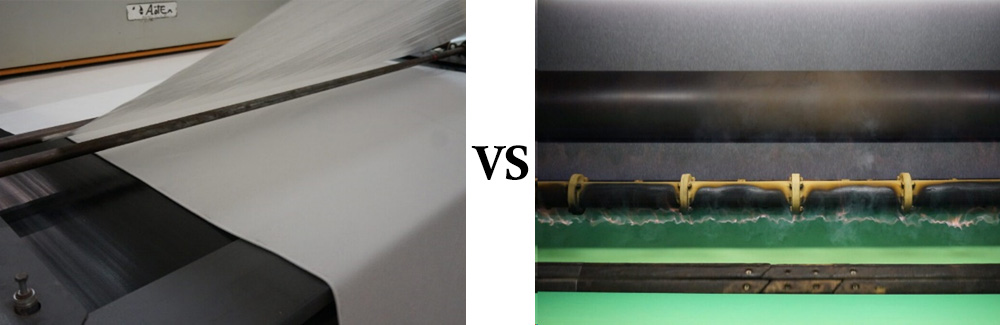
Flame Lamination
Flame lamination, also known as flame bonding or flame attachment, utilizes a controlled flame to melt and bond a laminating material to a substrate. Here’s a closer look at how it works:
- Process: The laminating material is unwound and passed over a flame.
- Bonding: The heat from the flame melts the foam which then serves as an adhesive on the laminating material.
- Application: As the material continues through the process, a pressure roller ensures that the melted adhesive bonds securely to the substrate.
- Cooling: The laminate is then cooled and wound onto a roll.
Advantages of Flame Lamination:
- High-Speed Processing: Flame lamination is known for its rapid processing, making it ideal for large-scale production runs.
- Strong Bond: The process creates a durable and robust bond due to the flame-melted adhesive.
- Versatility: This method is versatile and can be applied to a range of materials, including paper, fabric, and foam.
Disadvantages of Flame Lamination:
- Material Limitations: Flame lamination might not be suitable for sensitive or heat-sensitive materials.
Dal-Bac has staff with decades of experience that maximizes the quality and reduces safety issues while maximizing the range of materials that customers can select for flame lamination executions.
Thermal Fusing Lamination
Thermal fusing lamination, on the other hand, uses heat and pressure to bond a laminating material to a substrate. Here’s how this method operates:
- Process: The laminating material and substrate are placed between heated rollers.
- Bonding: The heat softens the adhesive on the laminating material, while the pressure from the rollers ensures a strong bond.
- Application: The resulting laminate is cooled and wound onto a roll.
Advantages of Thermal Fusing Lamination:
- Precise Control: Thermal fusing offers accurate temperature and pressure control, leading to consistent results.
- Safe Operation: With no open flames involved, this method is generally safer for operators.
- Material Flexibility: It is suitable for a broader range of materials, including those that are sensitive to heat.
Disadvantages of Thermal Fusing Lamination:
- Slower Processing: This method is typically slower compared to flame lamination, which might affect production efficiency.
Both flame lamination and thermal fusing lamination are effective methods for bonding materials, each with its own set of advantages and limitations. Flame lamination is excellent for high-speed applications and creating strong bonds, while thermal fusing provides precise control and enhanced safety. At Dal-Bac Manufacturing, we understand the importance of choosing the right lamination method to meet the specific project needs for all clients, regardless of location.
Consider your material type, production volume, and safety requirements to make the best choice for your application and reach out to Dal-Bac Manufacturing for an estimate on your next project. We’re here to help you find the perfect solution tailored to your needs.
